Laser can be divided into liquid laser, gas laser, and solid laser according to the medium of laser generation. The most common semiconductor laser is a kind of solid-state laser. Semiconductor lasers are electrically driven diodes.
Laser has a lot of parameters, but the main technical parameters include: wavelength, output power, working voltage, line width, line length, shape size, laser divergence Angle, spot mode, modulation mode, only know these main technical parameters, we can choose the laser we need.
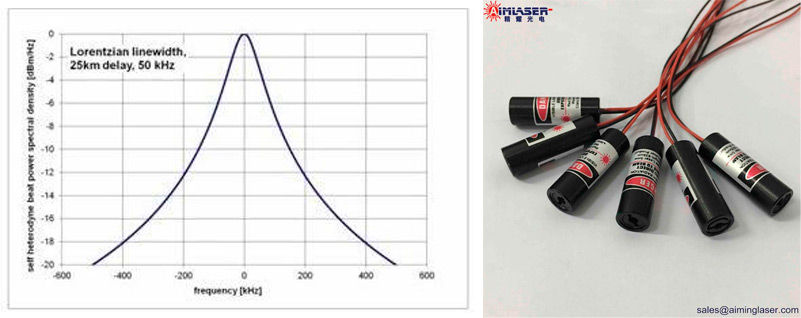
Laser linewidth, the full width of the half-height of the spectrum emitted by the laser source, that is, the width between the two frequencies corresponding to the half-height of the peak (sometimes also 1/ E). Light from the laser, laser vibration, there will be one or more longitudinal modes, the frequency range of each longitudinal mode is the laser line width. Note that the frequency width of each longitudinal mode and the interval between longitudinal modes are two different concepts. The longitudinal mode interval is the difference between the central frequencies of two adjacent longitudinal modes.
The laser linewidth is determined by the quality factor of the resonator, the higher the quality factor of the cavity, the narrower the laser linewidth. After considering the gain of the laser medium, the theoretical limit of the linewidth of the laser is determined by the spontaneous radiation of the gain medium. For example, for he-Ne, the theoretical limit of the linewidth is about the order of 10^-3Hz.
The linewidth is mainly affected by the spontaneous emission of excited atoms or ions, phase noise, mechanical vibration, and temperature jitter of the resonator. The smaller the line width, the higher the spectral purity, that is, the better the monochrome of the laser. Lasers with such characteristics usually have very little phase or frequency noise and very little relative intensity noise. At the same time, the smaller the line width of the laser, the stronger the coherence, which is shown as an extremely long coherence length.
Due to the limitation of the natural gain linewidth of the laser working material, the output of narrow linewidth laser can hardly be realized directly by the traditional oscillator itself. To realize the operation of the narrow-linewidth laser, it is usually necessary to use filters, gratings, and other devices to limit or select the longitudinal modulus in the gain spectrum and increase the net profit difference between each longitudinal mode so that there are a few or even only one longitudinal mode oscillation in the laser resonator. In this process, it is often necessary to control the influence of noise on laser output to minimize the spectrum broadening caused by vibration and temperature change in the external environment; At the same time, it can also be combined with the analysis of phase or frequency noise spectral density to understand the source of noise and optimize the design of laser, to achieve stable narrow linewidth laser output.

